Your Guide to a Complete Cotton Nutrition Program
February 10, 2022
Thanks for tuning in to our Cotton Fertility Program Webinar! Technical Agronomist, Greg Jackson, has put together his recommendations for the key nutrients needed at each growing stage for cotton that you can take to the field this season.
What You’ll Learn
- What nutrients are important to cotton
- What role those nutrients play in cotton production
- When to apply these nutrients
- Which products can help you accomplish your goals
In the video above, Greg will walk you through each growth stage for cotton. Below, you’ll find a summary of the information as well as some other helpful tips and tools.
Questions?
If you have any questions at all about this information presented to you, BRANDT is always glad to help. Click or tap the button below to get in touch with a BRANDT expert.
Do you think BRANDT’s products are the right fit for your operation? Click or tap the button below to find a retailer that sells BRANDT products near you.
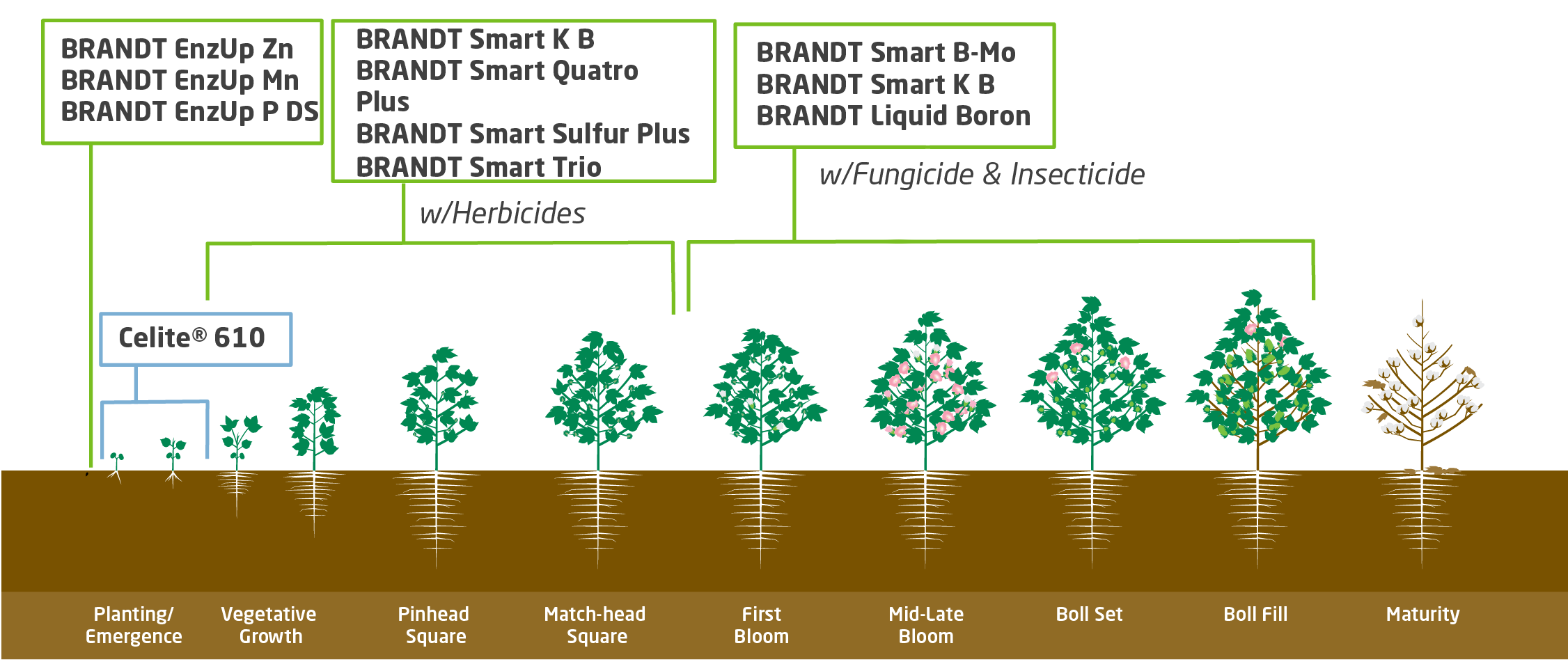
3 Goals for Cotton Fertility
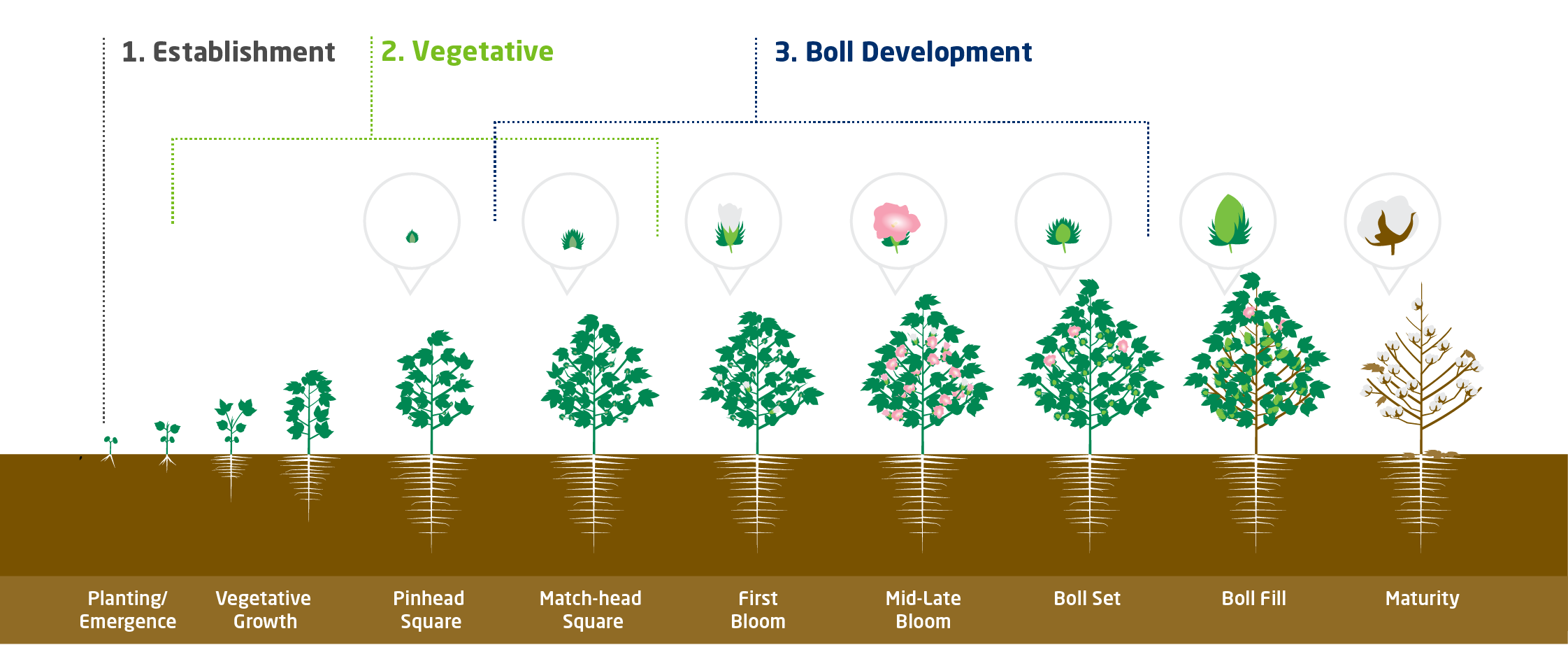
We've broken this fertility program into three goals that a grower should try to accomplish to optimize yield and set up the crop for a good yield next year. Within each of these goals we're going to focus on the role various plant nutrients play during those stages of crop development.
- Establishment
- Vegetative
- Boll Development
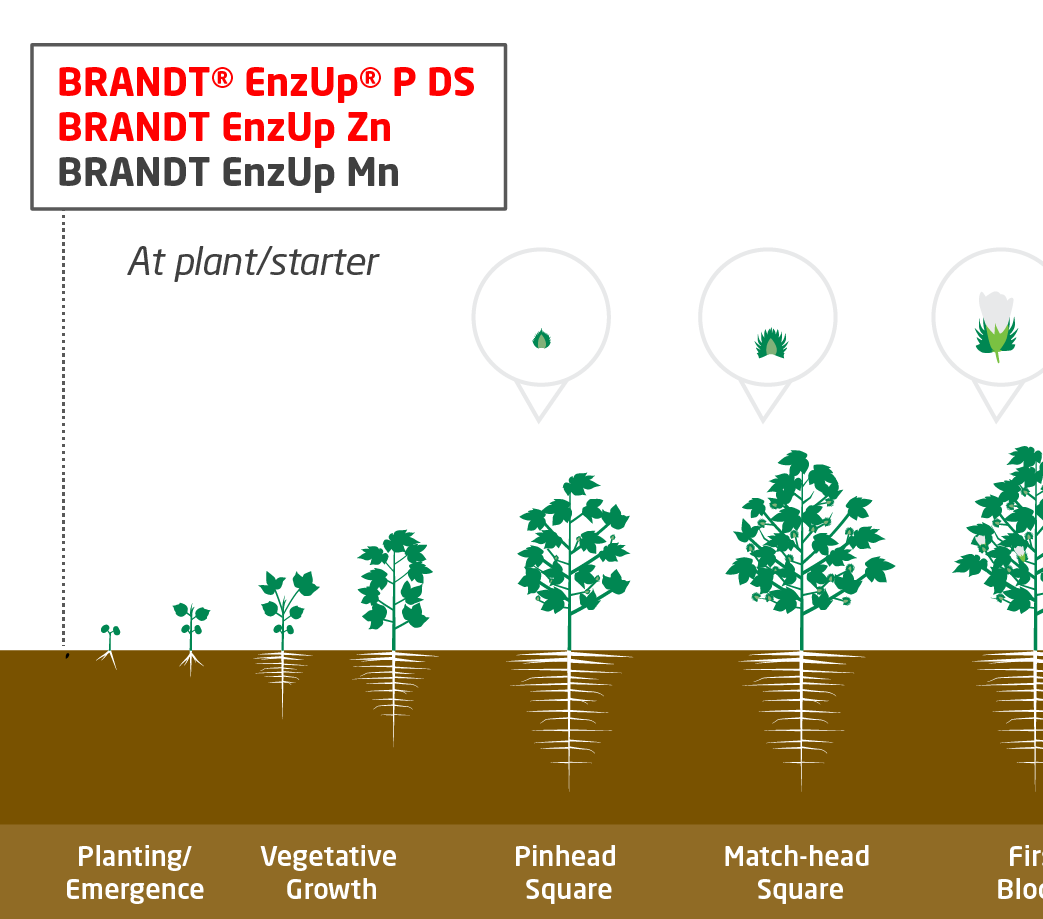
Establishment
Key Nutrients
- Zinc
- Manganese
- Phosphate
Products and Timing
- BRANDT EnzUp Zn 1 qt/acre (4.0% Zn)
- BRANDT EnzUp Mn 1 qt/acre (3.0% Mn)
- BRANDT EnzUp P DS 5-30 lb/acre (12.0% N, 58.0% P2O5)
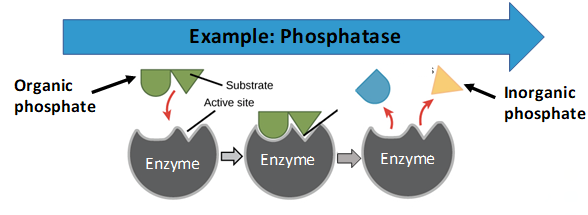
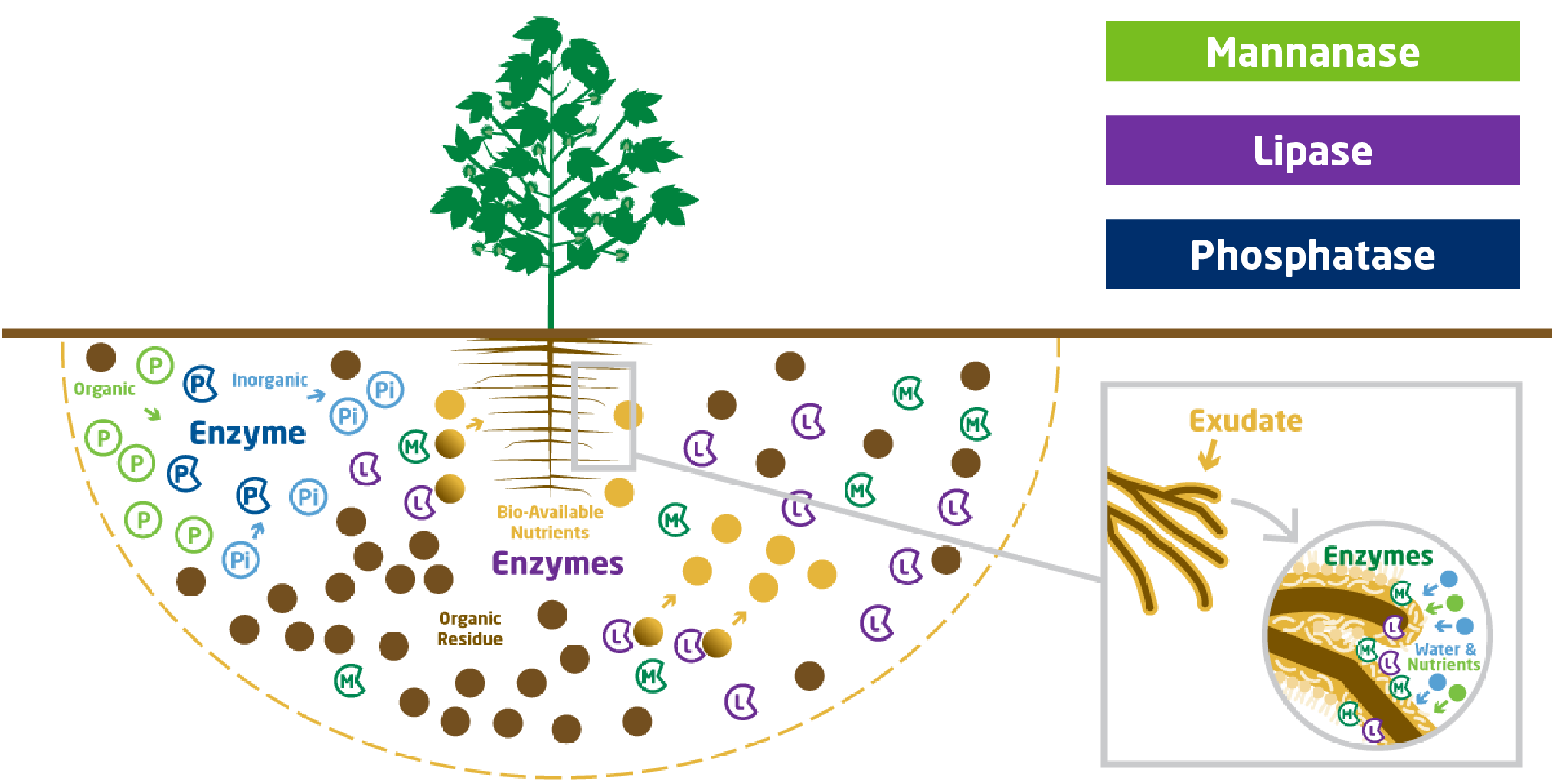
What are Enzymes?
- Proteins that catalyze biological reactions
- In the soil they are produced primarily by microbes and perform many important functions:
- Conversion of organic and inorganic nutrients
- Nitrogen fixation and conversion
- Carbon cycling
- Pesticide degradation
- Organic matter decomposition
- Many require metallic cofactor like Zinc to function
- ENZYMES ARE NOT ALIVE but... they can degrade under environmental conditions
Priming the Soil with BRANDT EnzUp Technology
MANNANASE: Breaks down exudates around root tip and organic carbon, which releases sugars and improves water and nutrient uptake
LIPASE: Breaks down lipid portion of organic matter into smaller more digestible units, potentially also mineralizing N and P into plant available forms.
PHOSPHATASE: Converts organic phosphorous into inorganic, making it available for uptake.
|
Product Name |
Fertilizer Analysis |
Formulation Type |
Enzymes Present |
|
BRANDT EnzUp Zn LS |
4% Chelated Zinc |
Liquid |
Mannanase, Lipase |
|
BRANDT EnzUp Mn LS |
3% Chelated Manganese |
Liquid |
Mannanase, Lipase |
|
BRANDT EnzUp K DS |
5-0-49-8S |
Dry Soluble |
Phosphatase, Mannanase |
|
BRANDT EnzUp S DS |
21-0-0-23S |
Dry Soluble |
Phosphatase, Mannanase |
|
BRANDT EnzUp P DS |
12-58-0 |
Dry Soluble |
Phosphatase, Mannanase |

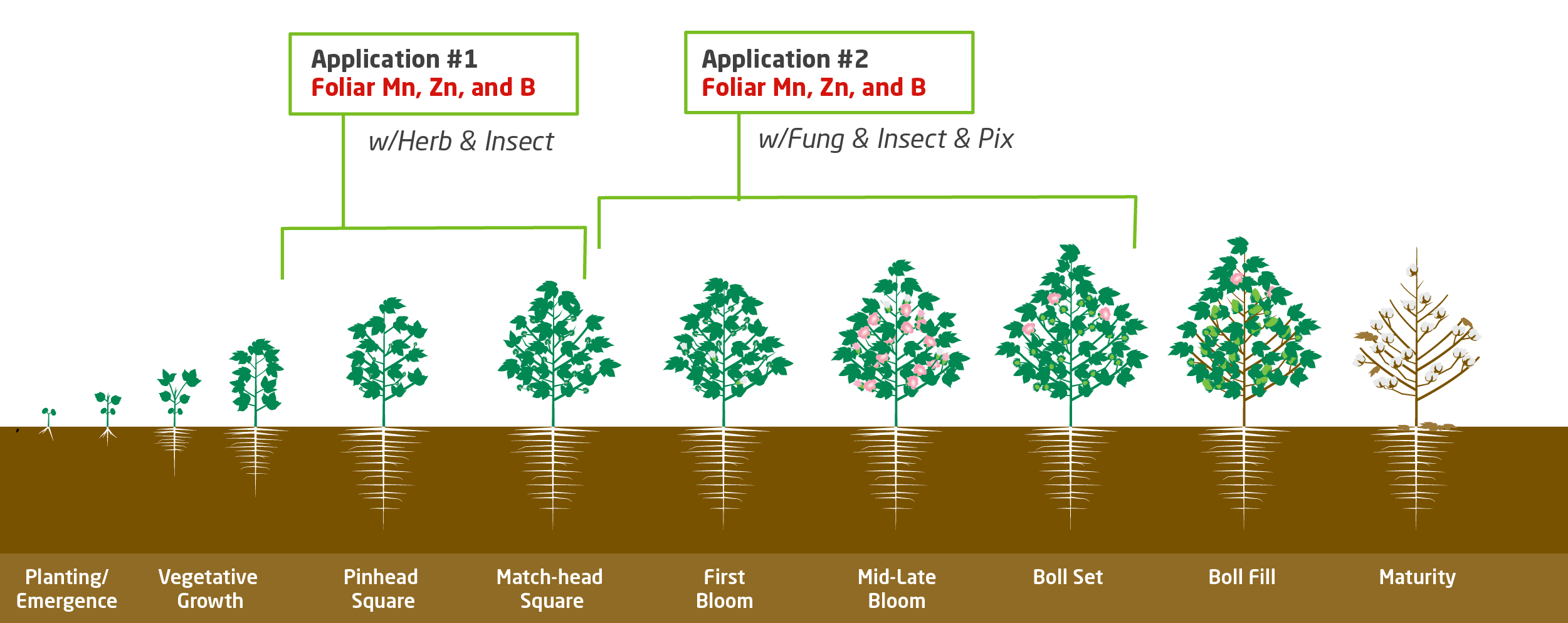
Key Timing for Foliar Mn, Zn and B on Cotton
- Many herbicides can have compatibility problems with Micronutrients. Product selection very important.
- Most Micronutrients products typically mix well with fungicides and insecticides in the Cotton market.
- Foliar Zn & Mn applications should be made approximately
10 to 14 days apart.
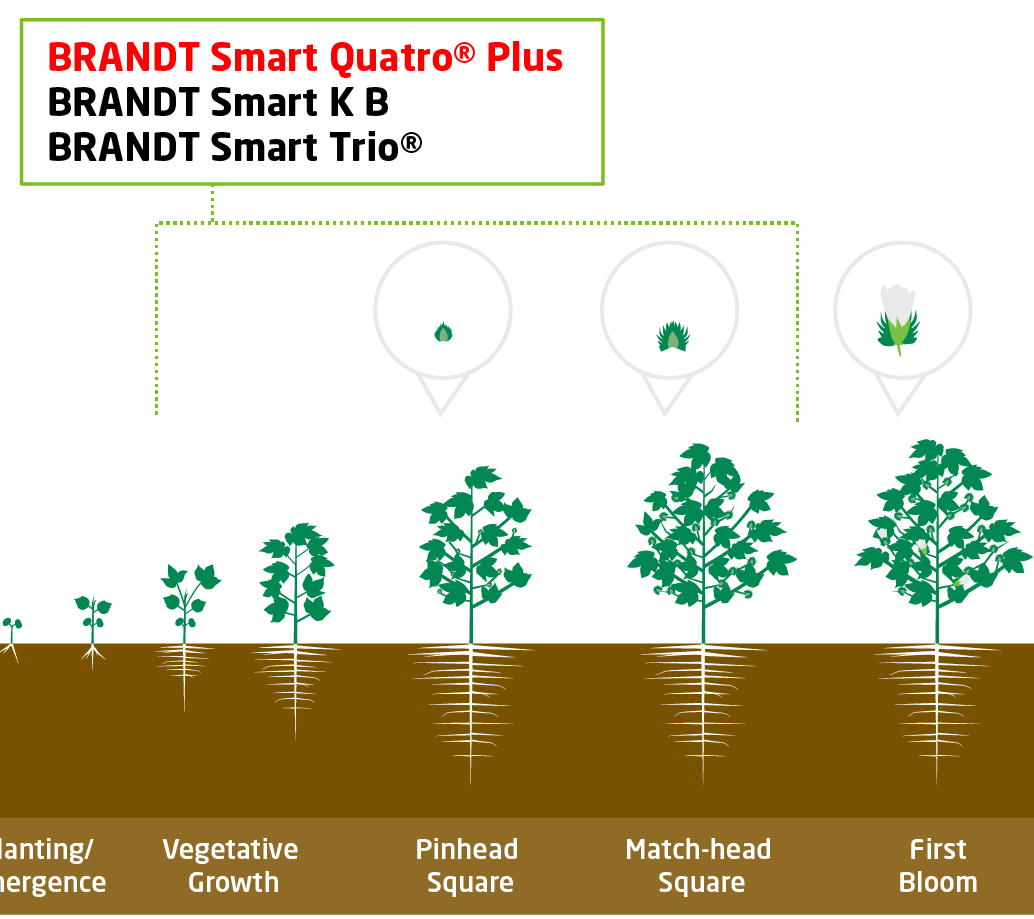
Vegetative
Key Nutrients
- Manganese
- Boron
- Zinc
- Sulfur
Products and Timing
- BRANDT Smart Quatro Plus 1-2 qt/acre (5.0% N, 2.0% S, 0.5% B, 2.0% Mn, 0.05% Mo, 2.0% Zn)
- BRANDT Smart K B 1-2 qt/acre (2.0% N, 16.0% K2O, 2.5% B, 0.2% Mo)
- BRANDT Smart Trio 1-2 qt/acre (4.0% N, 3.0% S, 0.25% B, 3.0% Mn, 3.0% Zn)
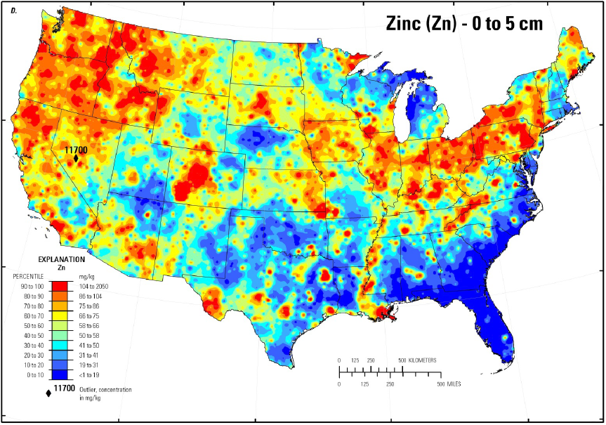
Critical Micronutrient Soil Levels in Cotton Growing Regions:
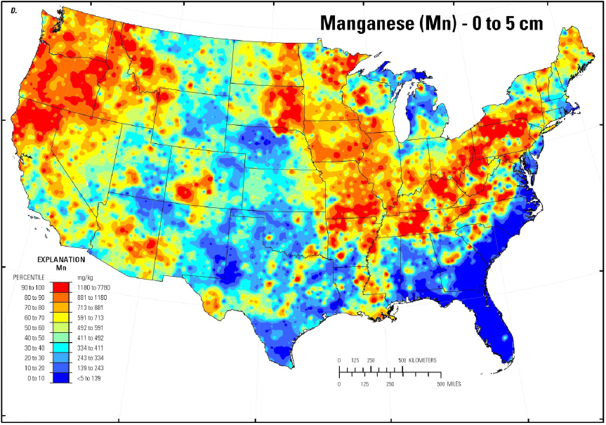
Fe, Mn, and Zn Are Inherently Low
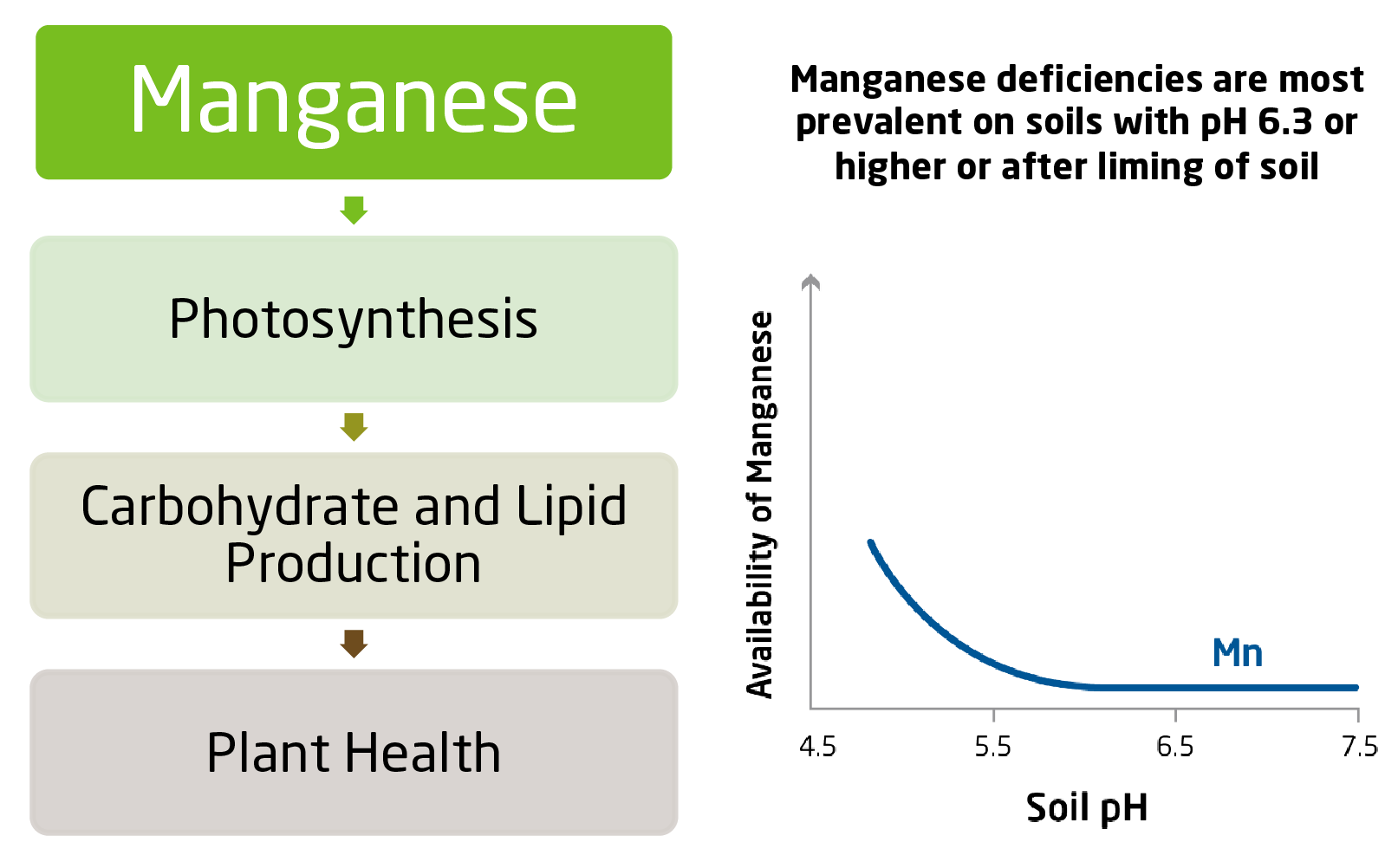
Manganese: Very Important to Plant Health and Photosynthesis
From the first squares to full bloom stages, manganese should be 50-350 parts per million.

Mn deficiency show up as yellowing between leaf veins at the top of the plant.
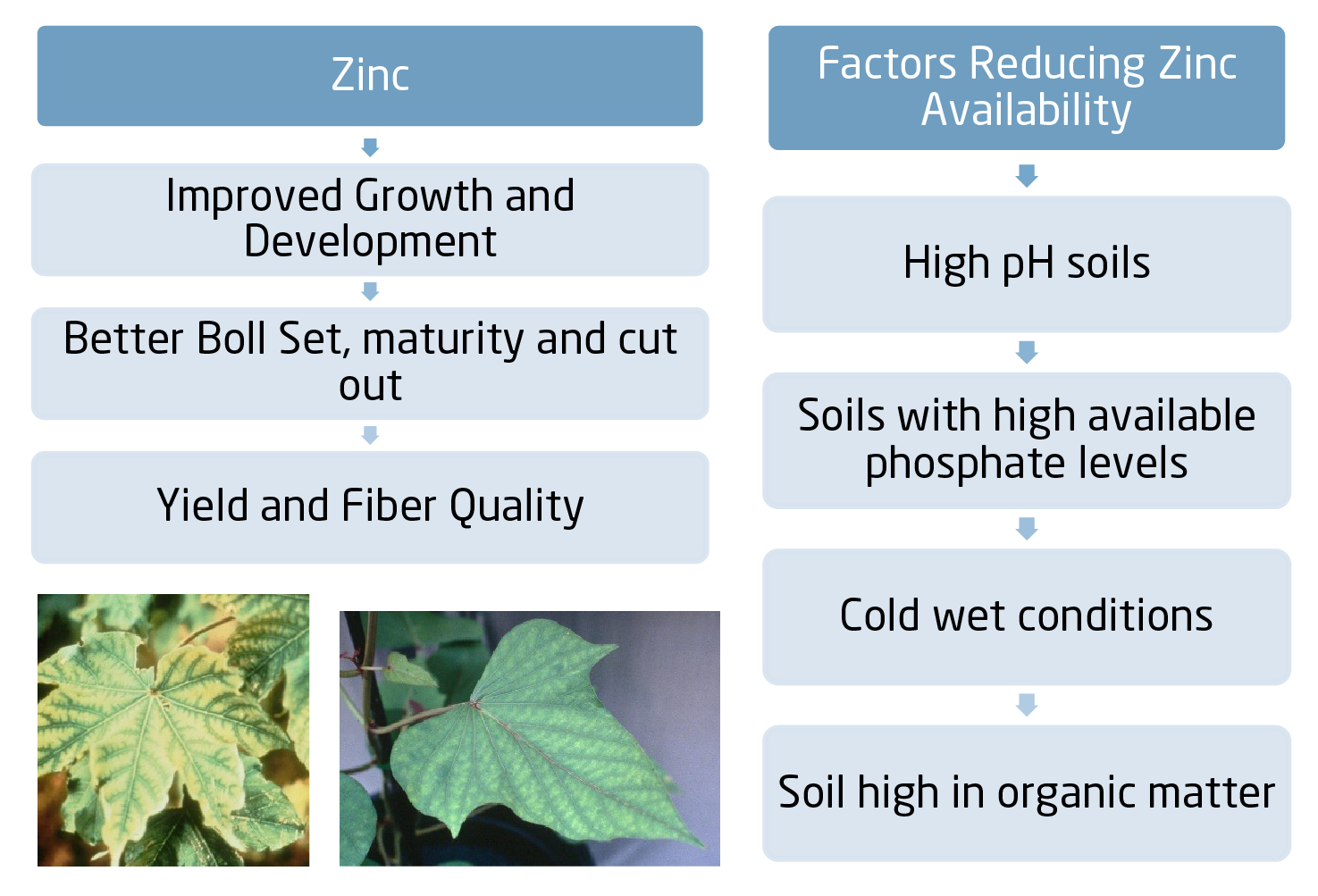
Zinc: Very Important to Plant Growth and Development
From the first squares to full bloom stages, zinc should be 40-200 parts per million.
Zinc Deficiency Symptoms
- Appear in younger leaves of upper canopy with interveinal chlorosis
- May include short internodes (resetting), small , stunted leaves with interveinal chlorosis,
BRANDT Smart System Advances Compatibility Foliar Nutrients
|
BRANDT Products |
Guaranteed Analysis |
Compatible w/ Cotton Herbicides |
Compatible w/ Fungicides & Insecticides |
|
BRANDT Smart Trio |
4.0% N, 3.0% S, 0.25% B, 3.0% Mn, 3.0% Zn |
N |
Y |
|
BRANDT Smart Mn |
6.0% N, 3.5% S, 6.0% Mn |
N |
Y |
|
BRANDT Smart Mn Plus |
5.0% N , 2.0% S, 4.0% Mn |
Y |
Y |
|
BRANDT Smart Sulfur Plus |
5.0% N, 5.0% S, 0.5% B, 1.5% Mn, 0.05% Mo, 1.5% Zn |
Y |
Y |
|
BRANDT Smart Quatro Plus |
5.0% N, 2.0% S, 0.5% B, 2.0% Mn, 0.05% Mo, 2.0% Zn |
Y |
Y |
BRANDT Smart Mn Plus, Sulfur Plus and Quatro Plus offers growers the flexibility to apply with early with herbicides to get ahead of issue for growers that have know micronutrient deficiency issues.

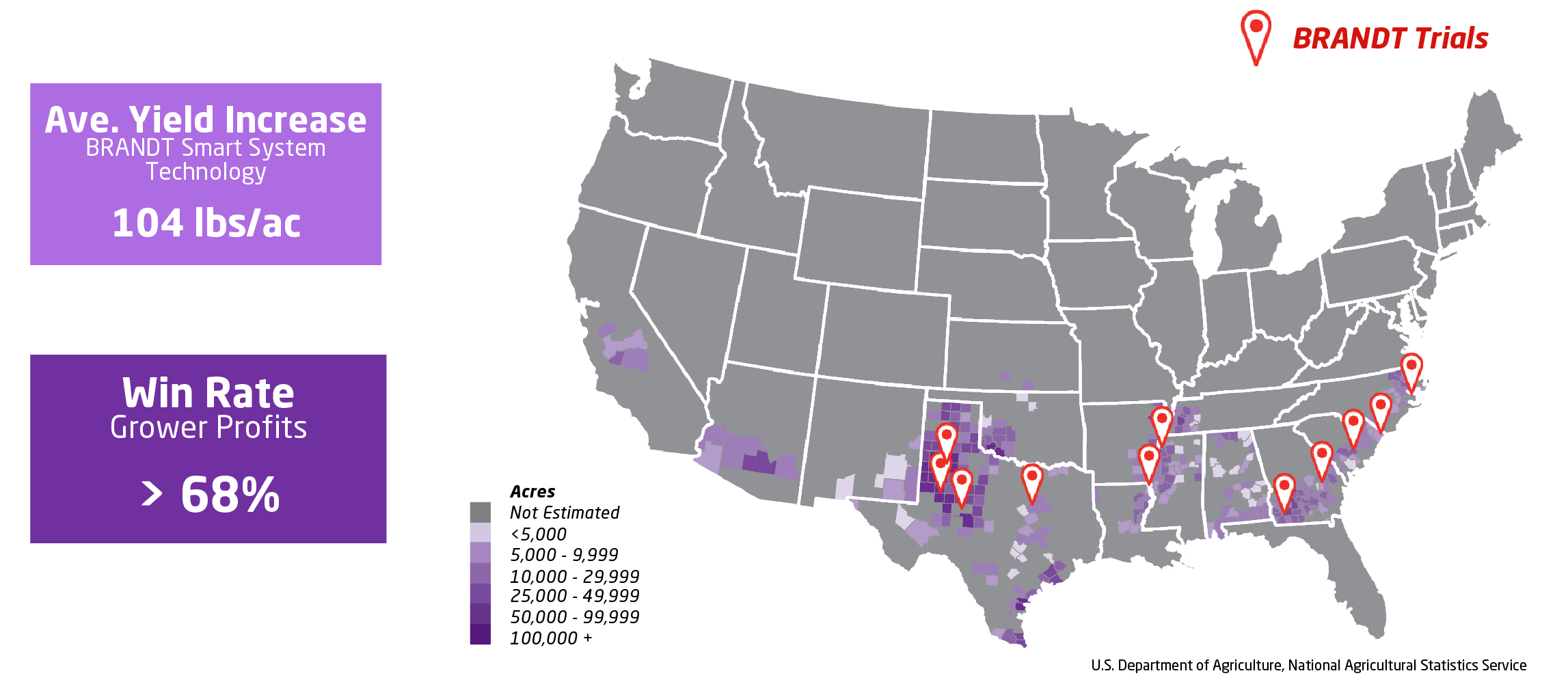
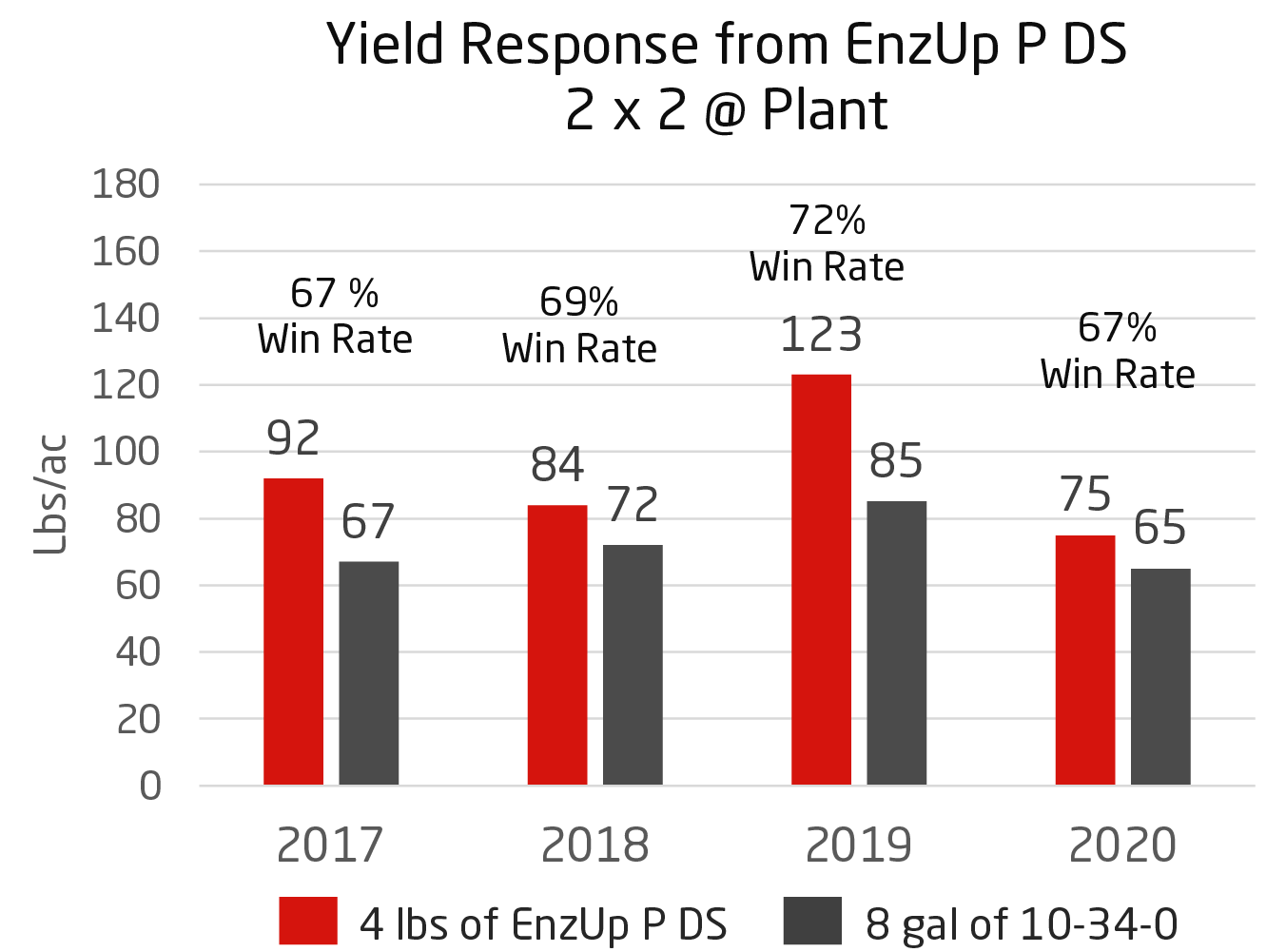
BRANDT Smart System Foliar Nutrient Performance on Cotton: Data Includes BRANDT Smart Trio, BRANDT Smart Mn, BRANDT Smart Quatro Plus, BRANDT Smart Mn Plus
Boll Development
Key Nutrients
- Boron
- Potassium
Products and Timing
- BRANDT Smart K B 1-2 qt/acre (2.0% N, 16.0% K2O, 2.5% B, 0.2% Mo)
- BRANDT Smart B-Mo 0.5 -1 pt/acre (5.0% N, 2.0% S, 4.0% Mn)
- BRANDT Liquid Boron 5 qt/acre (10% B)
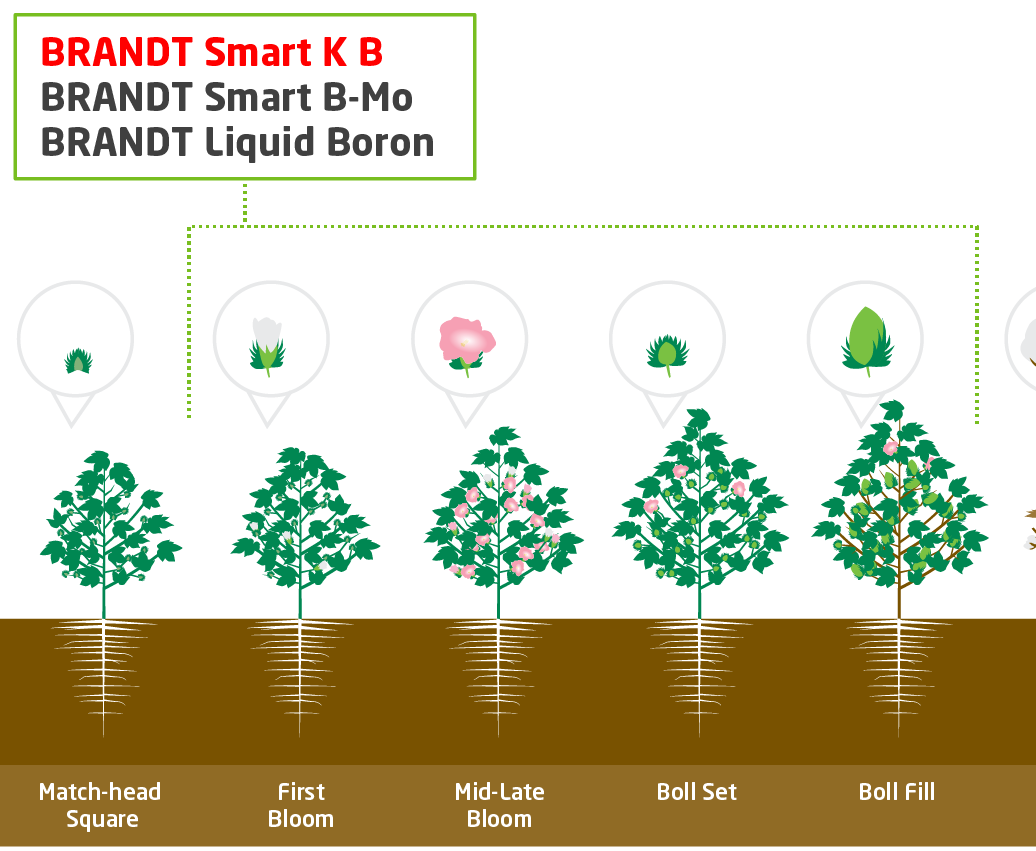
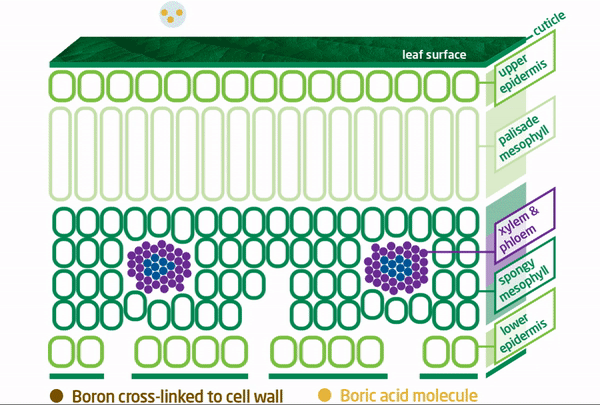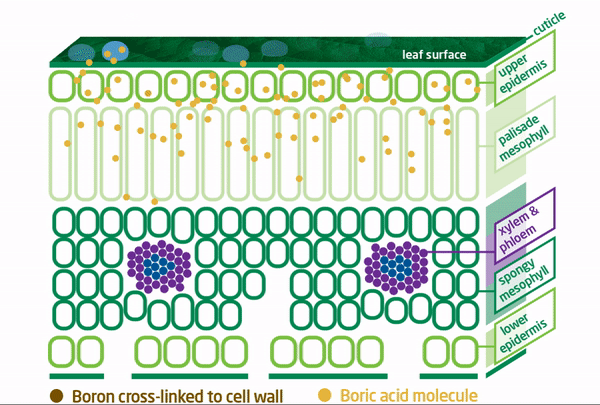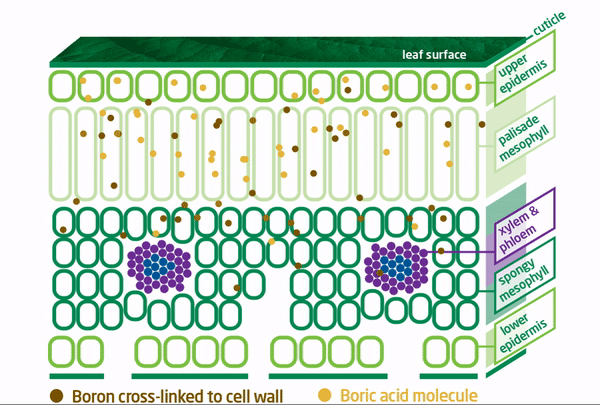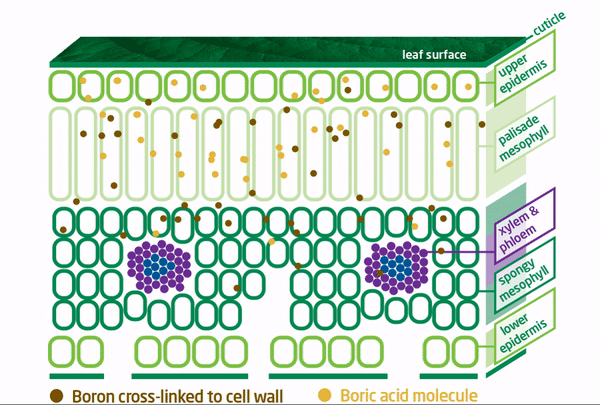
BRANDT Smart B Superior Mobility
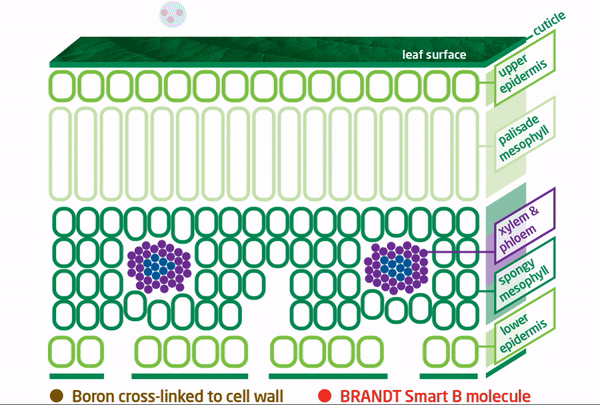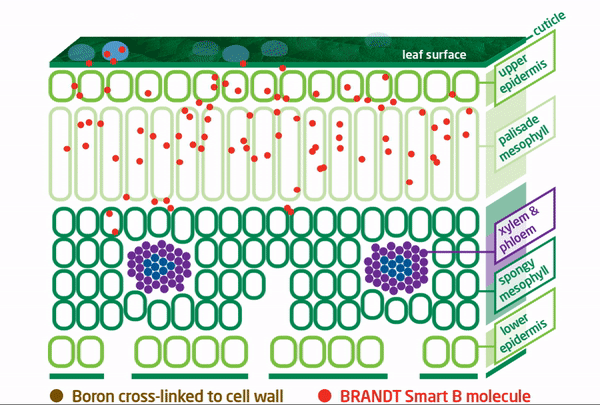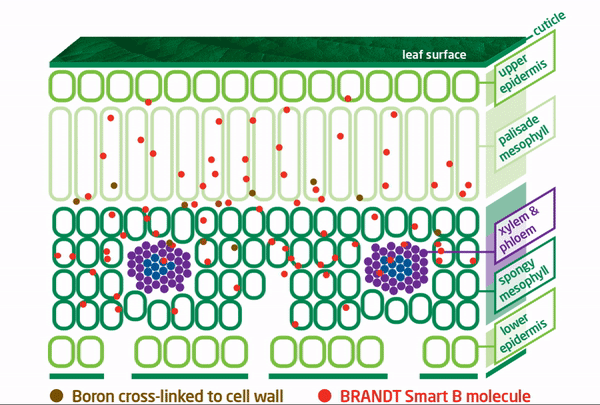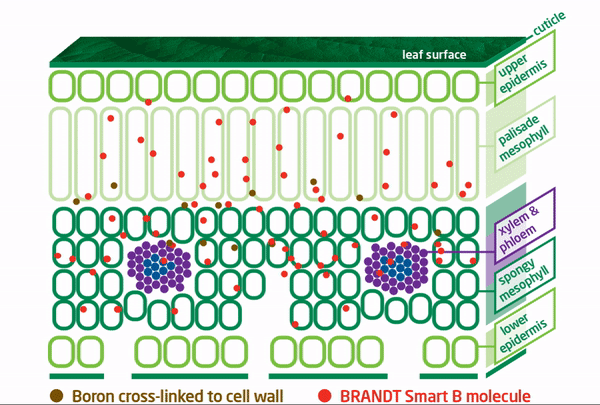
Conventional Boron Tied Up Inside Plant
Our Boron Moves!
Typically, once boron has been absorbed by the plant and incorporated into the primary cell walls structures, disassembly, reorganization, and transport of the boron cannot occur resulting in its immobility.
To address this boron mobility issue, BRANDT developed BRANDT Smart B and BRANDT Smart B-Mo to specifically prevent boron from binding with pectins, ensuring that applied boron remains free and mobile for effective travel to plant growth tissues.
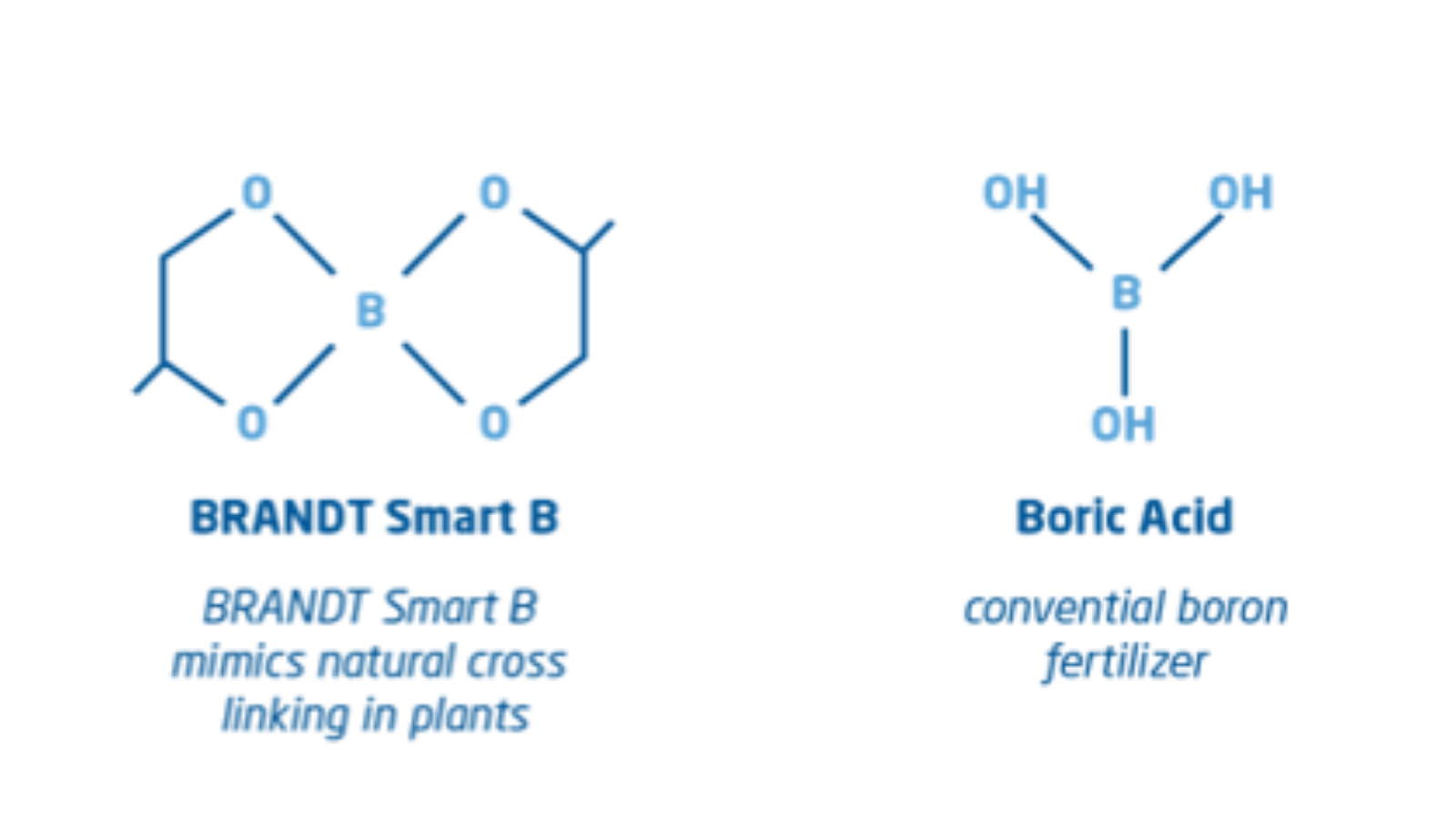
The BRANDT smart boron molecule is cross-linked, which provides a protective “shield” for the boron that significantly increases foliar applied boron mobility. This allows the smart boron molecule(s) access to plant growing points quickly and easily, thereby providing the most benefit.
The molecule structure also allows the formulations to tank mix with other crop chemicals and fertilizers, including calcium, without any compatibility issues.
In contrast, conventional boron fertilizers are not cross-linked with oxygen, which results in less boron availability and less boron at plant growing points
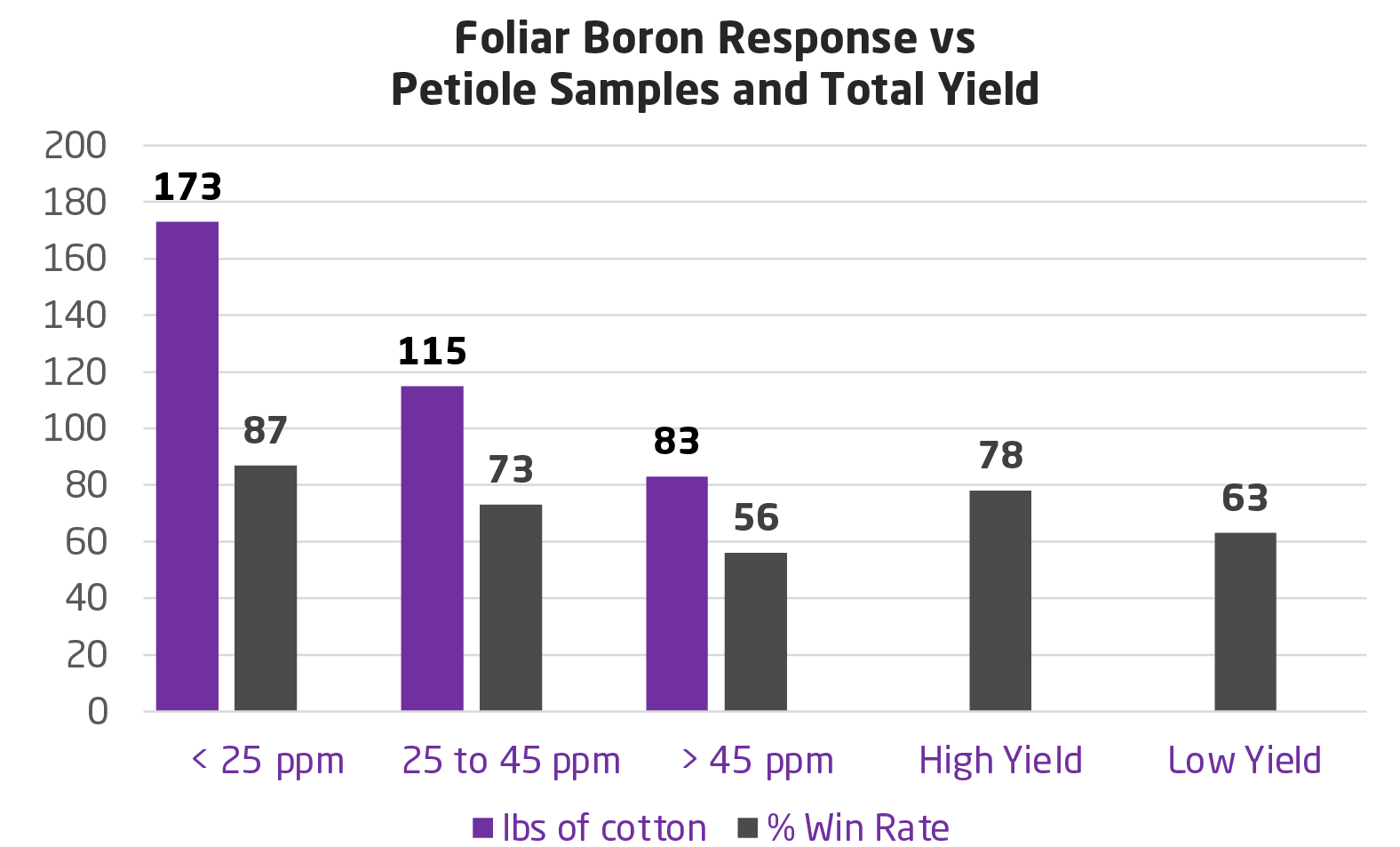
Foliar Boron Data on Cotton in the US2017 to 2020 - 42 different trial sites
- Responsiveness (%Wins) somewhat correlated to boron levels in crop.
- Also total yield potential plays a role.
- High yielding cotton has greater demand.
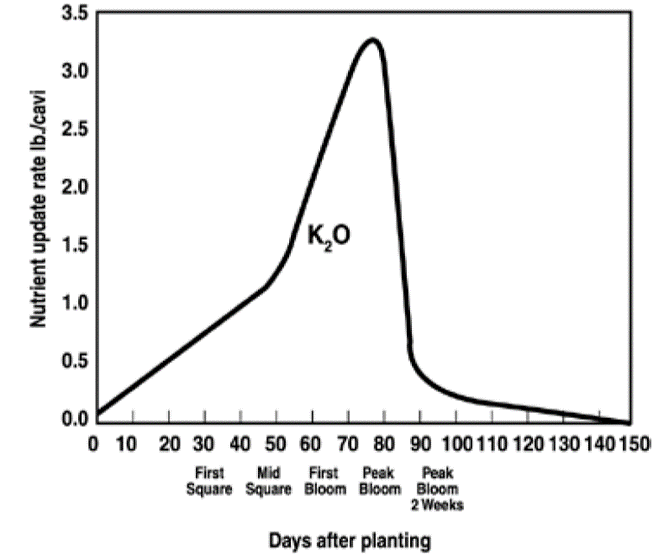
High Demand of K in Cotton Well Established
- High demand K of fruiting structures as a sink for K is well established.
- In high-yielding cotton varieties, as much as ¾ of the K is partitioned to fruiting structures (bolls).**
- Potassium has a key role in fiber quality and strength, which is not surprising since it is the most abundant mineral nutrient in fibers.
Figure shows nutrient uptake rates reached maximum during mid-bloom and declined rapidly as the boll matures (Mullins and Burmester. 1990.)
|
BRANDT Products |
Guaranteed Analysis |
Compatible With F&I |
Compatible with Manganese |
|
BRANDT Smart B |
5.0% B |
Y |
Y |
|
BRANDT Smart B-Mo |
5.0% B, 0.5% Mo |
Y |
Y |
|
BRANDT Smart K B |
2.0% N, 16.0% K2O, 2.5% B, 0.2% Mo |
Y |
Excellent |
|
BRANDT® Manni-Plex® K |
20% K2O |
Y |
Alkaline pH, not good for some insecticides |
|
BRANDT EnzUp K DS |
5%N, 49%K, 8.0%S (Dry Soluble) - Solutionized for Sidedress |
Y |
Y |
|
BRANDT Liquid Boron |
10% B (all 10% B have high pH) |
Y |
Jar Test |
These foliar K and B formulations have been tested and proven to be especially good on cotton.