The Importance of Zinc in Rice
August 18, 2021
Agronomics / Background
Micronutrients are important in order to help rice reach its full potential and zinc (Zn) is the most commonly deficient micronutrient both in rice and in soils. From an agronomic perspective, zinc is important to rice for a number or reasons:
- Nitrogen assimilation and protein metabolism – Approximately 10% of proteins in plants require Zn for structural function and integrity. Low Zn supply limits the rice plant’s ability to convert amino acids to proteins. Additionally, the rate of protein synthesis is drastically reduced in Zn-deficient plants.
- Auxin metabolism – Zn deficiency causes reduced auxin levels, leading to little leaf syndrome, stunted growth and reduced shoot elongation. An example is indole acetic acid (IAA). Indole requires Zn to produce tryptophan which leads to IAA. Reduced Zn leads to higher stress responses, causing production of more free radicals, leading to the degradation of IAA.
- Membrane structure, function and maintenance – Zinc deficiency can cause chlorosis by allowing the breaking down of chlorophyll.
- Carbohydrate metabolism
Conditions Leading to Zinc Deficiencies in Rice
Zn deficiency can lead to stunted plants, delayed maturity and reduced yield. It also makes leaves very sensitive to light and heat. Soil Zn availability is affected by a number of factors including pH, soil phosphorous concentration, organic matter, clay content, calcium carbonate levels, soil drainage and concentration of iron and aluminum oxides.
Zinc deficiency most often occurs in cold, wet spring weather and in rice symptoms commonly appear soon after flood. Symptoms are most often seen in new growth, making in-season foliar applications a good option for correction.
|
Crop: Rice |
|||
|
Stage: 25 mature leaves from new growth |
|||
|
Macronutrients % |
Micronutrients PPM |
||
|
N |
2.8 – 3.6 |
Fe |
75 – 200 |
|
P |
0.1 – 0.18 |
Mn |
200 – 800 |
|
K |
1.2 – 2.4 |
B |
5 – 15 |
|
Ca |
0.15 – 0.3 |
Cu |
8 – 25 |
|
Mg |
0.15 – 0.3 |
Zn |
25 – 50 |
|
S |
0.18 – 0.33 |
Mo |
1 - 5 |
*Bryson, Mills, et al. “Plant Analysis Handbook III”. 2014.
Key Application Timings and Rates for Zinc in Rice
- Foliar application of 1 – 2 quarts/acre of BRANDT® Smart Zn at tillering
- BRANDT's Smart System® products are formulated for use with most herbicides, insecticides and fungicides. Their small molecular structure allows for increased foliar uptake.

Zinc Deficiency Illustrations in Rice
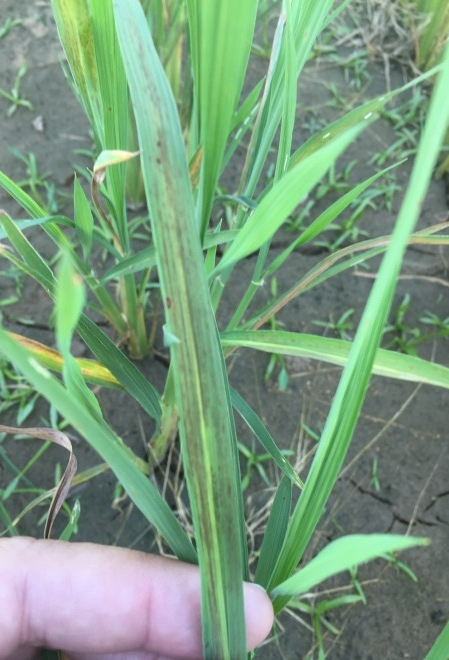

*Photo courtesy of www.agfax.com

*Photo courtesy of Louisiana State University
Trial Data
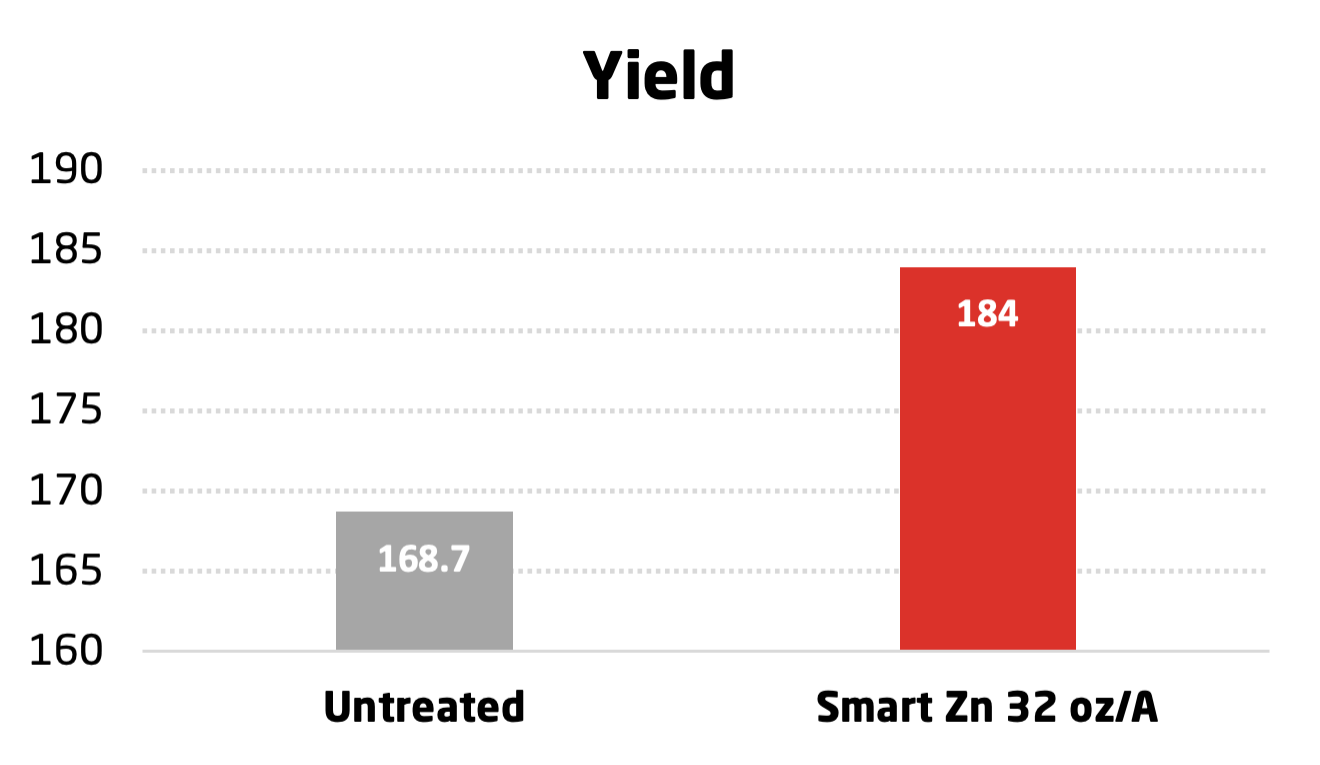
BRANDT Smart Zn Trial on Rice conducted in Winchester, AR in 2013.
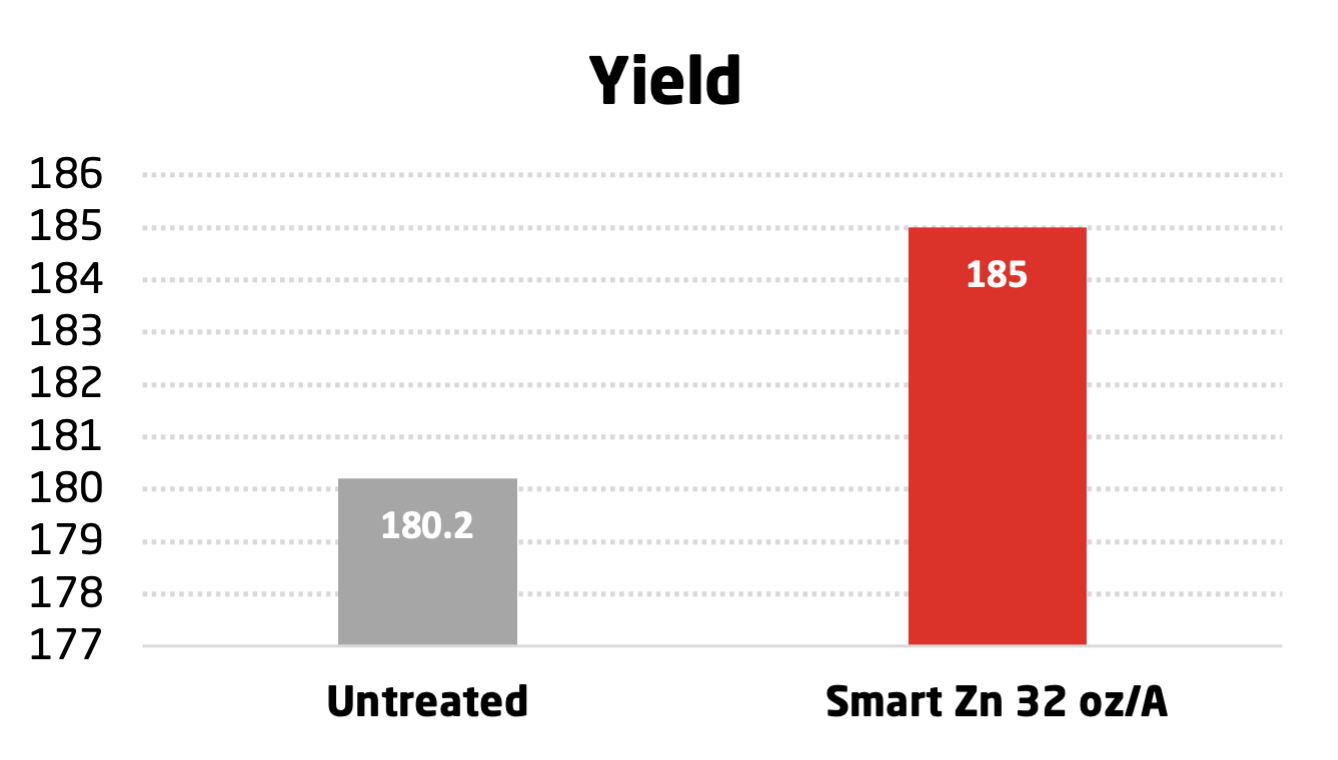
BRANDT Smart Zn Trial on Rice conducted in Marlanna, AR in 2014.
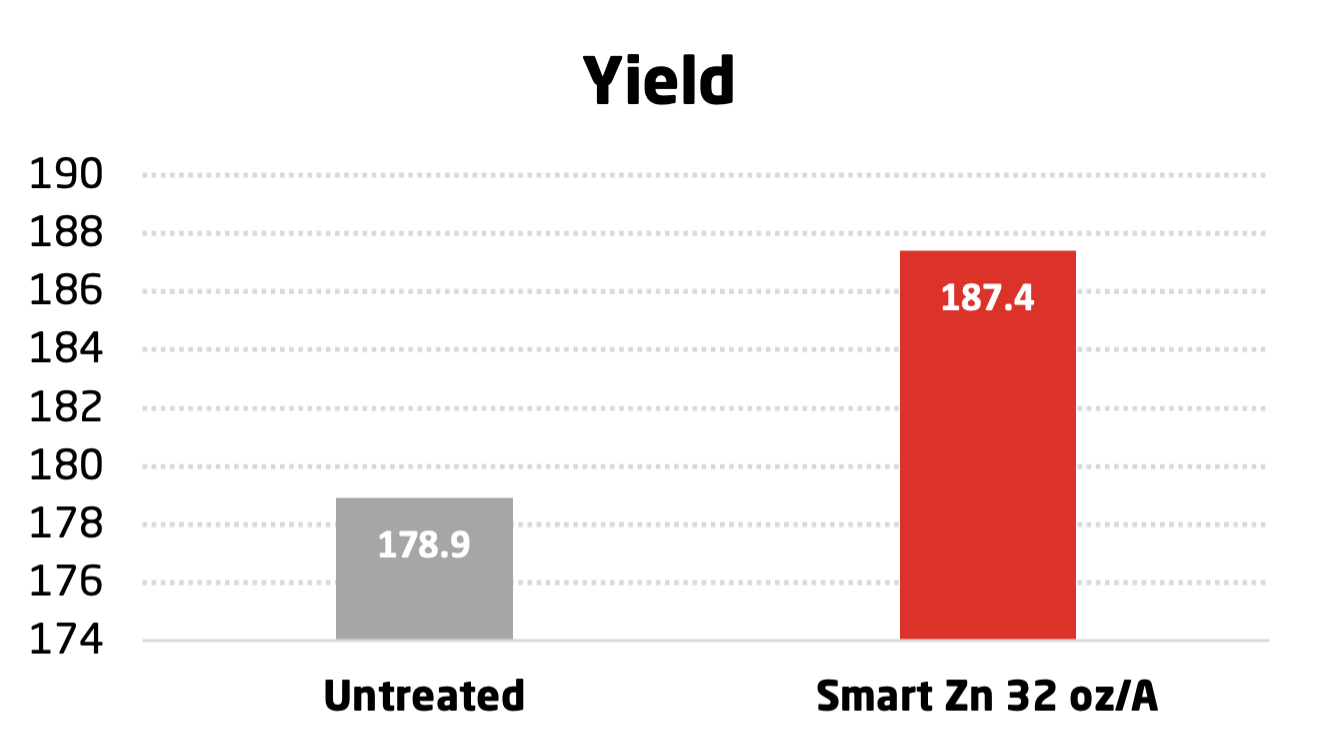
BRANDT Smart Zn Trial on Rice conducted in Winchester, AR in 2014
